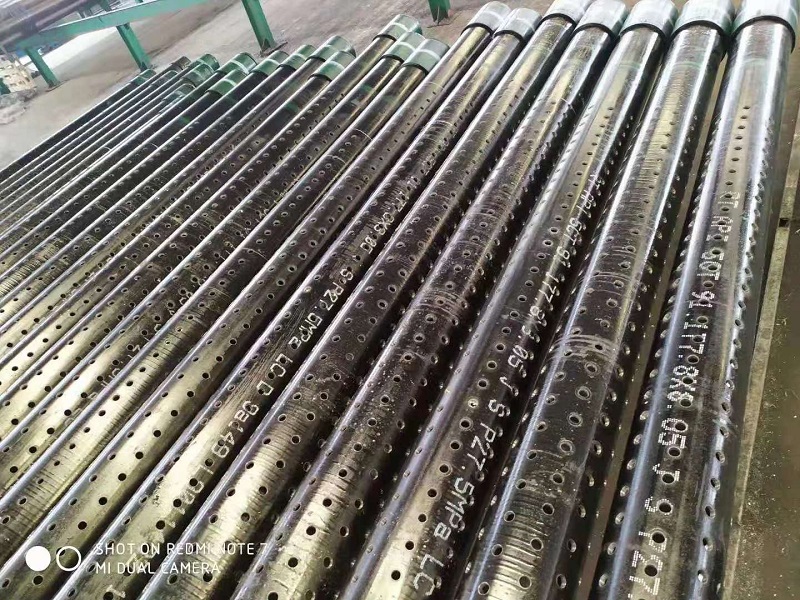
Classification of Piles Based on Transmission and Functional Nature
Piles can be classified into different types based on their transmission and functional nature. These classifications include:
- Friction Piles (Cohesion Piles): Friction piles derive their load-bearing capacity primarily from the frictional resistance between the pile and the surrounding soil. They transfer the load to a firm stratum located at a significant depth below the structure. The piles behave as a normal section and need to be designed accordingly. Even in weak soil, the piles do not fail due to buckling, unless a part of the pile is unsupported. The load is transmitted to the soil through friction or cohesion. However, in some cases, the soil surrounding the pile may adhere to its surface, causing “Negative Skin Friction” which can significantly affect the pile’s capacity. The depth of the pile foundation is determined by site investigation and soil testing results.
- End Bearing Piles (Point Bearing Piles): End bearing piles transfer their load to a firm stratum through the penetration resistance of the soil at the toe of the pile. These piles behave as a column and should be designed accordingly. They rely on the load-bearing capacity of the stratum beneath the base of the structure. Load is transmitted to the soil through friction or cohesion, depending on the specific conditions. In some cases, the soil may adhere to the pile surface, causing negative skin friction. The depth of the pile foundation is influenced by site investigation and soil testing.
- Combination of Friction and Cohesion Piles: This type of pile is an extension of end bearing piles when the bearing stratum is not firm, such as in soft soil. The pile is driven deep enough into the lower material to generate sufficient frictional resistance. Another variation is piles with increased bearing areas, achieved by injecting concrete into the soft stratum above the firm layer to create an expanded base. A similar effect can be achieved with bored piles by forming a large cone or bell at the base using a reaming tool. These bored piles with a bell have high rigidity and can be used as tension piles.
- Combination of Friction Piles and Cohesion Piles: This category includes piles that transfer load through both friction and cohesion. The process of driving these piles does not significantly compress the soil. They are commonly referred to as pile foundations.
By understanding the different types of piles based on their transmission and functional nature, engineers can select the most appropriate pile foundation for a given project, considering the soil conditions, load requirements, and structural design. Proper design and installation are crucial to ensure the effectiveness and performance of the chosen pile type.
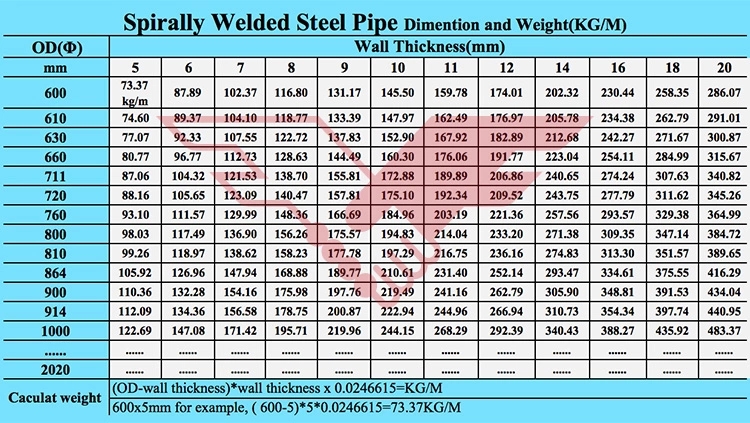
|
Product name
|
API 5L X52 piling steel pipes-SSAW Spiral welded steel pipes
|
|||
|
Standard
|
API 5L, EN10255, EN10219, EN10210, EN39, BS1387,
ASTM A53, ASTM A500, ASTM A36, ISO 65 JIS G3444,DIN 3444, ANSI C80.1, AS 1074, GB/T 3091 |
|||
|
Material
|
Gr.A, Gr.B, Gr.C,
S235, S275, S355, A36, SS400, Q195, Q235, Q345 |
|||
|
Finish of pipe
|
Hot dipped galvanized with zinc 220~260g/m2;
Painted with black/varnish lacquer; Oil on the surface to prevent rust; Bare pipe without painting: Epoxy painting/FBE coating/3PE coating |
|||
|
Applications
|
Construction / building materials steel pipe
Scaffolding pipe Fence post steel pipe Fire protection steel pipe Greenhouse steel pipe Low pressure liquid, water, gas, oil, line pipe Irrigation pipe Handrail pipe |
|||
|
Delivery Time
|
15-45 days (based on quantity) after receiving advanced payment by T/T or LC .
|
|||
|
Main Market
|
Southeast Asia, South Asia, Middle East, Europe,
Middle&South America, Africa and Oceania |
|||












