Overlap Sheet Pile: A Comprehensive Study
Introduction
Sheet piling is a construction technique used to support soil and water retention structures. It involves driving interlocking sheets of material, such as steel, into the ground to form a continuous barrier. Overlap sheet piling is a specific type of sheet piling where the sheets are overlapped rather than interlocked. This paper provides an in-depth analysis of overlap sheet pile, covering its history, materials, design considerations, installation techniques, applications, advantages, and limitations.
History of Sheet Piling
Sheet piling has been used for centuries to provide structural support for waterfronts, foundations, and other civil engineering projects. The earliest forms of sheet piling were made from wood, but as technology advanced, materials like steel and concrete became more common. The development of interlocking sheet piles in the early 20th century revolutionized the industry, offering greater strength and durability. Overlap sheet piling emerged as an alternative to interlocking systems, providing unique benefits in specific applications.
Overlap Trench Sheet or trench sheet piles have another name as Overlap Sesctions. It has been widely used in road construction projects.
Product Production Range:
Customized designs are also available and welcomed in our company.
Material: Q235B, Q345B, S235, S240, SY295, S355, S430, S460, A690, ASTM A572 Grade 50, ASTM A572 Grade 60. All Chinese Standard, EN Standard, ASTM Standard and other standard material are available on request.
Manufacturing & Inspection Standard: EN10249-1 / EN10249-2

Lapped trench sheets(M6,M8,M12,Multisheet 500/4,Multisheet 500/6,HY6,Shorco 500/6)
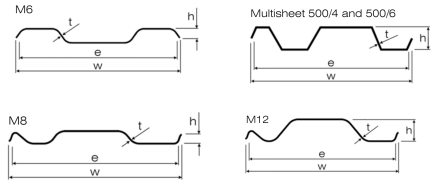
| Section |
Dimensions |
Mass |
Per meter of wall |
| Width |
Height |
Thickness |
Single
pile |
Wall |
Section
modulus |
Bending
Moment |
| e |
h |
t |
W |
I |
| mm |
mm |
mm |
Kg/m |
kg/m2 |
cm3/m |
KNm/m |
| M6 |
394 |
38 |
3.55 |
12.5 |
31.2 |
46.6 |
7.9 |
| M8 |
585 |
50 |
6 |
31.79 |
54.29 |
93 |
21.8 |
| M12 |
550 |
87.5 |
6 |
31.79 |
57.8 |
182 |
42.7 |
| Multisheet 500/4 |
480 |
75 |
4 |
21.1 |
44 |
125.8 |
40 |
| Multisheet 500/6 |
480 |
75 |
6 |
31.6 |
65.8 |
178.2 |
66 |
| HY6 |
520 |
69.4 |
6 |
33.7 |
64.8 |
160 |
63.2 |
| Shorco 500/6 |
500 |
52 |
6 |
28.5 |
57 |
97 |
22.3 |
Materials Used in Overlap Sheet Pile
Steel
Steel is the most common material used in overlap sheet piling due to its high strength, durability, and ability to withstand significant loads. Steel sheet piles can be hot-rolled or cold-formed. Hot-rolled sheets are produced at high temperatures and offer superior structural integrity, while cold-formed sheets are shaped at room temperature and are more cost-effective.
Concrete
Concrete sheet piles are used in situations where corrosion resistance is critical. They are typically pre-cast and reinforced with steel rebar. Concrete piles are heavier and more challenging to install than steel piles but offer excellent durability and resistance to environmental degradation.
Vinyl
Vinyl sheet piles are used in less demanding applications where corrosion resistance and ease of installation are prioritized. They are lightweight, easy to handle, and resistant to chemical and biological degradation, making them suitable for marine and waterfront applications.
Composite Materials
Composite sheet piles combine materials like fiberglass and resin to offer a balance of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. These materials are used in specialized applications where traditional materials may not perform well.
Design Considerations
Load Bearing Capacity
The primary function of sheet piles is to support loads from soil and water. The design must account for the maximum load the pile will bear, including static and dynamic forces. Engineers use soil mechanics principles and structural analysis to determine the appropriate sheet pile size and material.
Soil Conditions
Soil type and condition significantly impact the design and installation of sheet piles. Cohesive soils, such as clay, provide better support for sheet piles than non-cohesive soils, like sand. Engineers conduct soil tests to determine the soil’s bearing capacity, friction angle, and other properties that influence the sheet pile design.
Water Table
The presence of groundwater affects the design and installation of sheet piles. High water tables can increase the hydrostatic pressure on the piles, requiring more robust materials and designs. Engineers must also consider the potential for water seepage and the need for dewatering during installation.
Environmental Factors
Environmental considerations include the potential for corrosion, chemical exposure, and biological degradation. Materials like steel may require protective coatings or galvanization to prevent corrosion, while concrete and composite materials may be selected for their inherent resistance to environmental factors.
Installation Techniques
Driving Methods
- Impact Driving: Uses a pile driver to hammer the sheet piles into the ground. This method is effective for driving piles through hard or dense soils.
- Vibratory Driving: Uses a vibrating head to shake the piles into the ground. This method is less noisy and can be faster than impact driving, but it may not be suitable for all soil types.
- Press-in Method: Uses hydraulic jacks to press the piles into the ground. This method is quiet and causes minimal ground disturbance, making it suitable for urban areas.
Overlapping Technique
In overlap sheet piling, the sheets are placed adjacent to each other with a small overlap, typically 50-100 mm. This overlap ensures a continuous wall without the need for interlocking joints. The overlapping technique requires precise alignment and handling to ensure the sheets are properly positioned and secured.
Joint Sealing
To prevent water seepage and ensure structural integrity, the joints between overlapping sheets must be sealed. Sealants, such as bitumen or rubber strips, are applied to the overlap area before driving the sheets into the ground. This sealing process is critical in water-retaining structures and areas with high groundwater levels.
Applications of Overlap Sheet Pile
Waterfront Structures
Overlap sheet piles are commonly used in waterfront structures, such as seawalls, bulkheads, and retaining walls, to protect against erosion and provide structural support. The corrosion resistance of materials like concrete and vinyl makes them ideal for these applications.
Foundation Support
In construction projects, overlap sheet piles provide temporary or permanent support for excavations and foundations. They prevent soil movement and water infiltration, ensuring a stable work environment and protecting adjacent structures.
Related Posts
ERW piling pipe | ERW Steel Pipe Pile | Welded ERW for Structure

ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) pipe piling is a type of steel pipe that is commonly used in construction and foundation applications, such as in the building of bridges, wharves, and other structures. ERW pipe piling is created by using a process in which a flat steel strip is rolled into a tube shape, and then the edges are heated and welded together using an electric current. ERW pipe piling has a number of advantages over other types of piling, including: Cost-effective: ERW pipe piling is generally less expensive than other types of piling, such as seamless pipe piling. High strength: ERW pipe piling is highly resistant to bending, making it a strong and durable option for foundation applications. Customizable: ERW pipe piling can be manufactured to meet specific size and length requirements, making it highly customizable and adaptable to different project needs.ERW Pipe Piling is available in a range of sizes and thicknesses, and can be produced in lengths of up to 100 feet or more. It is typically made from carbon steel or alloy steel, and can be coated with a layer of protective material to help prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of the pipe. Versatile: ERW pipe Read more
ASTM A252 Pipe Pile

WELDED Steel Pipe Piles (ERW ,LASW, DSAW ,SSAW.) The two most common methods for steel pipe welding are straight seam or spiral seam welding. Welded steel pipes are typically used to transport fluid (water or oil) and natural gas. It is typically less expensive than seamless steel pipe. Both types of welding are applied after the pipe has been rolled, which involves shaping a sheet of steel into the end shape. Straight Seam: Straight seam welded steel pipes are manufactured by adding a welding parallel to the pipe seam. The process is fairly straightforward: Straight seam pipes are formed when a sheet of steel is bent and formed into a pipe shape, then welded longitudinally. Straight seam pipes can be submerged arc welded (SAW) or double-submerged arc welded (DSAW). Spiral Seam: Spiral seam welded pipes are manufactured when hot-rolled strip steel is formed into a pipe through spiral bending and welded along the then spiraled seam of the pipe. This results in the weld length being 30-100% longer than that of a straight seam welded pipe. This method is more commonly used on large diameter pipe. (Note: this method of welding may also be referred to as helical submerged arc Read more
SSAW Pipe Pile | Spiral Weld Steel Pipe Pilings

Spiral weld pipe pile, otherwise known as SSAW Pipe pile, is a type of pipe piling product used in the construction of deep foundations. It is made from steel that has been formed into a spiral shape and welded together. It is used in a variety of applications, including bridge foundations, retaining walls, deep foundations for buildings, dams, and other large structures. Spiral weld pipe pile is a high-strength, low-alloy steel pipe made from a combination of rolled steel plates and helically wound steel strips. It is highly resistant to corrosion and has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal choice for deep foundations and other high-load applications. The process of creating spiral weld pipe pile begins with hot-rolling a steel plate into a coil. This coil is then fed into a machine which shapes it into a spiral shape. This spiral is then cut into sections and welded together to form a single pipe pile. After the welding is complete, the pipe pile is then heat treated and tested to ensure it meets the desired specifications. Spiral weld pipe pile is a strong and reliable choice for any deep foundation or other high-load application. It is resistant to Read more
The technical transition of spiral welded steel pipe piles, ASTM A252, EN10219, AWWA C200

Introduction Steel pipe piles have been used for many years as a foundation element in various construction projects. They are commonly used in the construction of bridges, buildings, and other structures that require a strong and stable foundation. The use of steel pipe piles has evolved over the years, with new technologies and techniques being developed to improve their performance and durability. One of the most significant advancements in the use of steel pipe piles is the transition from traditional steel pipe piles to spiral steel welded pipe piles. This paper will explore the technical transition of steel pipe piles to spiral steel welded pipe piles, including the benefits and challenges associated with this transition. PDF Downloads:Tubular Pile, pipe piles, steel piles, tubular pipes Background Steel pipe piles are typically made from steel plates that are rolled into cylindrical shapes and welded together. They are commonly used in deep foundation applications where the soil conditions are poor or where the structure being built is heavy. Steel pipe piles are typically driven into the ground using a pile driver, which forces the pile into the soil until it reaches a predetermined depth. Once the pile is in place, it provides Read more
ASTM A252 Standard Specification for Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Piles

Standard Specification for Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Piles1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 252; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval. 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers nominal (average) wall steel pipe piles of cylindrical shape and applies to pipe piles in which the steel cylinder acts as a permanent load-carrying member, or as a shell to form cast-in-place concrete piles. 1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions of the values in inch-pound units to values in SI units. 1.3 The text of this specification contains notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. Such notes and footnotes, excluding those in tables and figures, do not contain any mandatory requirements. 1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 16 of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated Read more
Steel Pipe Piles / Steel Pipe Sheet Piles
Steel pipe piles and steel pipe sheet piles have found extensive applications in various construction projects, including ports/harbors, urban civil engineering, bridges, and more. These versatile piles are used in the construction of piers, seawalls, breakwaters, earth-retaining walls, cofferdams, and foundations for steel pipe sheet pile foundations. With the increasing size of structures, deeper water depths, and construction work on sites with deep soft ground, the usage of steel pipe piles and steel pipe sheet piles has expanded significantly.











